Cryptocurrency is more popular than ever. But even as the number of cryptocurrencies available rises, Bitcoin still remains the king.
Bitcoins are created through a process called mining. Bitcoin mining serves two functions – validating new transactions on the Bitcoin network and bringing new BTC into circulation. Bitcoin miners are responsible for validating transactions and securing the Bitcoin network. Though mining can be a great way to acquire BTC, making a profit from the practice in 2026 is significantly more difficult than it used to be. This guide will explore how Bitcoin mining works in Australia and if you can still profit from it.
You can buy Bitcoin in Australia on Swyftx.
A brief overview of Bitcoin
Bitcoin has been a cornerstone of the cryptocurrency industry since it sprang to life in 2009. The creator of BTC, Satoshi Nakamoto, is a prominent figure in the crypto space but remains completely anonymous to this day despite widespread speculation on who it could be.
In 2010, the first Bitcoin transaction was recorded by a man named Laszlo Hanyecz. Hanyecz purchased two pizzas for a total of 10,000 BTC, which at the time was only worth roughly $60 AUD. The moment became etched into crypto history as “Bitcoin Pizza Day”.
By 2011, Bitcoin was no longer the only cryptocurrency in operation. Competitors such as Litecoin (LTC) and Namecoin (NMC) arrived on the scene.
By the end of 2017, Bitcoin had put in its all-time high, exceeding $25,000 AUD.
In 2021, Bitcoin’s price skyrocketed to a new all-time high in November in the industry’s most impressive bull market to date.
In 2022, Bitcoin remained the top crypto by market cap and saw some major upward spikes in spite of the overall market’s mediocre performance. However, by the end of the year, the price of one Bitcoin had plummeted to barely a quarter of its 2021 all-time high.
As history suggests, Bitcoin doesn’t stay down for too long. 2023 was a mixed year for the market as a whole, but one marked by steady gains for Bitcoin. The seminal coin nearly doubled in value from the start of the year without much hype or fanfare.
And 2024 was an even more positive year for Bitcoin, with the coin surpassing the US $100k mark, receiving approval for sport BTC ETFs and setting several new all-time highs.
This just reinforces that Bitcoin is still the most important digital currency and will likely stay that way for some time.
To gain more insight into Bitcoin check out our guide to Bitcoin, on Swyftx Learn.
How does Bitcoin mining work?
The underlying technology that supports Bitcoin is a decentralised database called a blockchain network. Blockchain technology functions as a peer-to-peer network that records transactions on a public ledger. For these transactions to be recorded and received by the recipient, they must be verified as legitimate. This is where Bitcoin miners come into the picture in a confirmation process referred to as consensus.
Therefore, Bitcoin mining is the process of confirming a group of transactions on the Bitcoin network. For such transactions to be confirmed, a complex mathematical problem needs to be solved by computers known as nodes. Bitcoin miners compete to solve these mathematical problems first. When the batch of transactions has been verified, they become a block that is recorded on the Bitcoin network.
Each time a block is created and added to the blockchain, the miner is rewarded with a predetermined amount of freshly mined Bitcoin.
Bitcoin is a unique asset as only a finite amount can ever be created. Bitcoin has a maximum supply of 21 million – 19 million of which has already been mined. In a process called halving, the reward for successfully validating a block gets smaller over time to ensure the supply of BTC doesn’t run out too quickly. Experts have predicted that the last bitcoin will be mined in 2140.
The deflationary supply mechanism is a key reason why similarities are often drawn between Bitcoin and Gold due to the scarcity of the assets.
Bitcoin halving
Another unique element of Bitcoin’s supply comes through the embedded code that halves Bitcoin’s block reward every four years (every 210,000 blocks). In the first years of Bitcoin, miners would receive 50 BTC each time they successfully validated a batch of transactions.
In 2012, the reward halved to 25 BTC, then 12.5 BTC in 2016 and finally 6.25 BTC in 2020. The next halving event occurred in 2024, with the block reward falling to 3.125 BTC.
At first glance, the amount of BTC rewarded dropping may seem like a disincentive to miners. However, the supply and demand metrics of Bitcoin mean that fewer BTC are entering circulation after each halving event. Assuming demand for BTC remains stagnant, the further restriction on supply puts upward pressure on Bitcoin’s price. Historically, halving events have resulted in fairly significant value spikes in the 6-12 months following.
What does a transaction confirmation involve?
To understand how Bitcoin mining works it’s important to understand the role of a Bitcoin miner. A Bitcoin miner’s job is to solve a ‘Hash’ code, which is created using a cryptographic protocol (hence why it’s called cryptocurrency).
A cryptographic hash is an algorithm applied to data to securely mask it. Essentially, it is a form of encryption. In cryptocurrency, the data being masked is the transaction details. Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 algorithm for hash functions which was designed by the United States National Agency in 2001. The SHA-256 algorithm generates an almost unique code from a text phrase or data file that’s been input, using a hash function.
It looks something like this:
ef537f25c895bfa782526529a9b63d97aa631564d5d789c2b765448c8635fb6c
This transaction hash code not only contains information related to a current transaction but also the transaction prior to it. Therefore, this additional information allows a miner to verify that the transaction occurred in a particular sequence on the blockchain. Once this confirmation has been made, the receiving wallet accepts that the transaction has occurred and is sent its Bitcoin.
The Hash power of a mining setup or mining rig will determine the capacity for conducting these confirmation tasks. More information about this will be covered below.
Cryptographic hash function
Types of Bitcoin mining
There are various ways to mine Bitcoin in Australia in 2026. The two most common options for mining Bitcoin are:
- Personal mining
- Cloud mining
Personal mining
Personal mining, also known as GPU mining, is the process of mining crypto through a personal computer. This is most often done through a Graphics Card Unit (GPU), but the rising popularity of Bitcoin mining of late has seen a broader selection of compatible computer hardware become available.
Standalone mining-specific hardware units are also available, like the Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC mining). ASIC miner chips are specially designed for mining crypto and are more efficient in producing hashing power compared to a regular computer.

ASIC Miner Unit
ASIC miners can vary in cost based on their output and mining efficiency. The technology underpinning such mining machines is evolving, and advancements in hardware and design typically result in superior performance.
While an ASIC miner gives an individual a better shot at successfully solving a hash function, it is still incredibly difficult to obtain a reward due to the competitive landscape of cryptocurrency mining. Therefore, personal miners will often utilise their output by being a part of a Bitcoin mining pool. A mining pool is a collective of Australian miners that work together to increase their chances of receiving a block reward.
If you’re mining Bitcoin in Australia, it’s crucial to select a reputable and established mining pool and understand the payout and fee structure of its membership.
Cloud mining
For aspiring miners in Australia, a Bitcoin cloud mining service can seem an attractive option due to its low barrier to entry. However, cloud mining also has its downsides.
Cloud mining involves a customer purchasing, or renting, a piece of physical mining hardware located in a professional facility (also referred to as mining farms).
‘Leased Hash Power’ is the most common type of cloud mining. This allows a user to purchase computing power from a mining farm. The customer is then able to take a cut of the overall profits while assisting in the maintenance and running costs of the mining farm.
The most important aspect of these mining options is the ‘breakeven point.’ This is a business term that occurs when you make the same amount of money from cloud mining as you put into it. It is extremely difficult to make a profit as an individual cloud miner, as the amount of Bitcoin rewarded to a miner will drop over time.
Mining difficulty is a metric referring to the average time taken to mine new blocks. This figure can regularly fluctuate as it is assessed and automated by the Bitcoin network depending on the number of miners participating. This will inherently govern how likely you are to be rewarded for all your efforts – and recently mining difficulty has become a lot more… well, difficult.
There are very few instances in Australia where cloud mining contracts can be profitable. In most cases, more profit can be generated by buying Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies compared to cloud mining.
Cloud mining hardware can also be very expensive, so some cloud mining services will mitigate costs by using renewable energy to mine crypto. These platforms give you access to cloud-based mining of coins such as BTC, DASH, LTC, ZEC, and XMR.
If adamant about becoming a cloud miner, be sure to perform due diligence on cloud mining services to avoid potential scams.
Is Bitcoin mining profitable?
Bitcoin mining can still be quite profitable in 2026, however, it was far more profitable in the earlier days of the cryptocurrency. Even though the performance yield of current technology is far better than it was, the competition and difficulty of earning rewards from mining has similarly increased. The potential for profitability is purely based on the costs of mining vs rewards output relative to difficulty at any given time.
Bitcoin mining consumes large amounts of electricity due to the power required for mining hardware to perform. If you are considering mining at home, you will need to be prepared for your electricity bill to rise. These costs can be mitigated by purchasing top-of-the-line hardware – but even the best mining equipment still eats a substantial amount of electricity. On top of this, the costs of electricity around the world have risen significantly since 2020, making it even harder to spin a profit.
Ocassionally, solo miners can get lucky and mine a block for its full reward on their own – as we saw several times throughout 2025. However, according to The Block, the chances of a solo miner repeating this feat is 1 in 30,000 every day. To put that in context, it would take the average participant 82 years to successfully solve a BTC block.
Ultimately, the decision will come down to each user and how much they want to invest. Typically, the more expensive the equipment, the better the earning potential. A good idea for those considering mining Bitcoin is to use a profitability calculator which can help determine daily, weekly or monthly profits (or losses) based on electricity costs and hardware available.
There is still room for improvements with current technology, especially with ASIC equipment and software, as new developments and improvements will result in further efficiencies in the power consumption costs and hash power output. It’s possible the next generation of mining machines will make big strides in cost-effectiveness.
Here are other reasons why mining is still profitable in 2026:
- More powerful hardware gives an advantage over older hardware users.
- Lower barrier of entry into renewable electricity options (solar).
- More trustworthy pools are becoming available and becoming a member will help miners earn income.
Related: How to invest in Bitcoin
Bitcoin mining difficulty in 2026
Mining difficulty is a metric of determining how difficult it is to mine a Bitcoin block. This difficulty scale is adjusted every two weeks, or every 2016 blocks, meaning the average time between blocks is ten minutes. Bitcoin mining difficulty dropped significantly in 2021, due to China’s cryptocurrency crackdown. Past indicators have suggested that around 70% of the world’s Bitcoin mining took place in China prior to the government-led crackdown. Despite the crackdown, Bitcoin mining was able to surge in other countries, causing the mining difficulty to hit an all-time high in early 2022 and continue that trend moving into the mid 2020s.
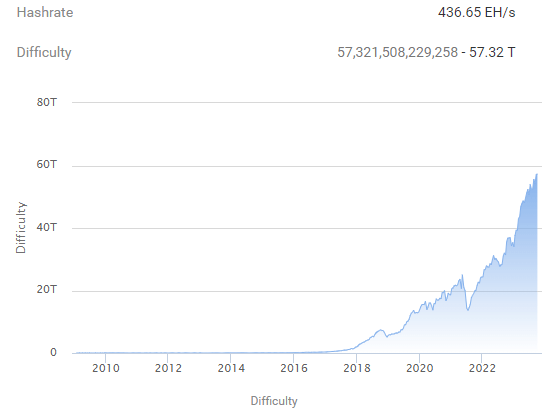
Bitcoin mining difficulty on January 21, 2022. Source Bitcoin.com
However, this was only the beginning of Bitcoin’s difficulty rising. Between 2022 and late 2023, the difficulty more than doubled as more and more miners tried to pick up the slack left behind by outlawed Chinese mining farms. By 2026, Bitcoin’s network difficulty had increased almost five times since late 2022.
How to mine Bitcoin in Australia
There are two primary ways to mine Bitcoin in Australia:
Method 1: Mining Bitcoin in Australia through a cloud mining platform
- Select a mining service provider. Compare various platforms for cloud mining and consider the contracts and costs/fees associated. Do your own research to find out if they are a reputable cloud mining provider.
- Choose a mining package/contract. After reviewing, check how long the mining contract will last. Aside from that, consider the mining hardware that the provider is using and compare that to what is on offer by competitors.
- Select a reputable mining pool. After purchasing the plan, many cloud mining services will need their users to pick a pool. Comparing different pools is necessary as well, so make sure to consider the track records and real user reviews.
- Store BTC. Once you’ve started mining, it’s recommended to store your Bitcoin in a BTC hardware wallet.
Method 2: Mining Bitcoin at home through personal hardware
- Calculate profitability. Before you start mining Bitcoin, it is recommended that you utilise a mining calculator. This will give you a good indication of the profits you’re likely to earn with the hardware you are using.
- Select the mining hardware. Comparing various hardware features, such as power consumption vs hash output, is crucial before deciding what to use. Also consider the cost of mining devices for ASIC vs a GPU/CPU setup, alongside your budget.
- Select a mining pool. Comparing different pools is a necessary step, so ensure to check out each pool’s track record and real user reviews.
- Download mining software. There are many programs for crypto/Bitcoin mining. Some software can be more technical to use, while some may provide a more user-friendly interface. Mining pools may also provide or suggest a particular software to use.
- Store BTC. Once you start mining, it’s recommended to transfer all earnings to a safe BTC wallet. It is important to note, regular maintenance is also completed on your mining system, as per the recommendations.
How to choose the best Bitcoin mining hardware
There are a few key factors to consider when choosing the best crypto mining rigs, namely, hash rate and energy consumption. Both determine the effectiveness and cost of mining cryptocurrency.
Hash rate
Hash rate represents the number of calculations the mining hardware can perform per second. A higher hash rate will boost the chances of solving a calculation first, resulting in sealing off the block and earning you a reward.
Hash rate can be measured in mega hashes per second (MH/second), gigahashes per second (GH/second) or terahashes per second (TH/second). For Bitcoin, the range is from 336 MH/s to 14,000,000 MH/s.
Energy consumption
Another factor to consider for those who want to mine Bitcoin in Australia is energy consumption. There is a critical relationship between hash rate and power consumption when calculating profitability.
The formula is dividing the hash count by the total power watts.
For example, if your rate is at 4.500 MH/sec, and it needs 32 power watts, you’ll have 140.625 MH/sec on every watt.
There’s also an online calculator available to estimate your power bill using hardware. It’s important to refer to your own power costs, as these vary around Australia and the world.
Find out more if Bitcoin is energy efficient.
Choosing the best Bitcoin mining software
When selecting the best crypto mining software, it’s important to check if your mining equipment has any software requirements that need to be installed before use.
The software client will control the hardware and how it conducts mining activities. This will be primarily used for solving transaction blocks.
Here are some of the best crypto mining software in 2026:
- NiceHash – This software has a user-friendly interface, and it runs on both macOS or Windows. It is an excellent choice for beginners, but can be a little expensive with a 2% fee.
- EasyMiner – This software supports different protocols for both pool and solo mining, along with performance graphs. It’s compatible with Linux and Windows only.
- Kryptex– A Windows app that pays you for the computing power of your PC.
- CGMiner – This software features a new block-self-detection, which comes with a mini database. It also includes CPU and multi-GPU support and fan speed control. The systems where it’s compatible include Linux, macOS, and Windows.
Understanding Bitcoin mining pools
In the modern landscape of Bitcoin mining, a large proportion of Bitcoin blocks are mined by pools rather than individual miners. This is why you should consider if you’re going to mine alone or participate in a pool.
Mining pools allow crypto miners to share their computing power with a collective group of miners in order to efficiently seal off blocks and lock in rewards. They do this because there is a greater chance of solving a calculation when hashing power is combined. However, the block reward will be split among members of the pool, usually proportionate to their input. This mechanism might be appealing as a stable income with a modest reward.
How to interpret mining difficulty and value earned
A Bitcoin block takes approximately ten minutes to mine. This metric is also referred to as the average confirmation time and is the proxy for mining ‘difficulty.’
Mining difficulty is a dynamic parameter that informs miners of the necessary computing power required for block mining. The difficulty score for Bitcoin changes after every 2016 blocks.
Some of the factors to consider when understanding mining difficulty include:
- The hash rate of the hardware among competitors
- The present and future anticipated reward for sealing a block
- The historic and present mining difficulty in projecting future difficulty
- The current market price for Bitcoin, and the number of transactions across the network
Guide to Bitcoin wallets
A Bitcoin wallet is a necessity for miners. BTC wallets provide access to your own wallet’s private keys that allow for complete ownership and safe storage of your digital assets.
Read: Best Crypto Wallet in Australia
Risks of digital wallets
- Using a wallet via digital exchanges runs the risk of being subject to cyber-attacks; some platforms may also have underlying security issues.
- Installing digital wallets can also be risky, as someone may be able to log in to your email or mobile phone and take control of that wallet.
- Digital wallets can be prone to viruses. When a user encounters malicious software, they can scan a hard drive to locate the private keys or hold your assets at ransom.
Tips for using a digital wallet
When using a digital wallet, be sure to do your own research to find the safest option available. Make sure you create a secure password and be careful when opening emails, as some scam emails may appear legitimate. There are many trusted and well-respected crypto wallets in the community, ranging from feature-laden to extremely simple. Most, but not all, digital wallets can innately store BTC, so make sure that they are compatible before creating an account.
A common recommendation is to use a hardware wallet, which is a crypto wallet that does not require an internet connection. This makes it much harder for hackers to access your hard-earned cryptocurrency. Ledger is the best and most reputable hardware wallet provider in the crypto wallet industry. The trade-off is inaccessibility (the wallet must be plugged into a PC to be used) and costs.

FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Can I mine other cryptocurrencies aside from Bitcoin?
Yes, it’s possible. There are several ‘Proof of Work’ digital assets including Dogecoin and Litecoin. Some of these mineable assets are more accessible and profitable than Bitcoin due to less competition.
What’s the amount of power necessary for mining BTC?
The electricity consumption of mining BTC is dependent on the hardware the miner chooses. The hardware used also determines the amount of power that is required to yield a reward from mining. According to Canstar, the average electricity cost per kWh across Australia is more than 25 cents per kWh. It should be noted this can change depending on your location.
How to start mining BTC
To start mining BTC you will need specialised hardware to ensure you are mining at a cost-effective rate. Mining hardware is continuously improving, with new products having better output and performance. You can also look to lease computer hashing power via cloud mining services.
Is Bitcoin mining legal to do in Australia?
Yes, it’s legal in Australia, as long as you are using your own electricity.
Is Bitcoin mining taxed by the ATO?
Yes, profits generated from mining Bitcoin are taxed by the ATO. There are various jurisdictions with their own regulations for digital assets regarding income, sales, payrolls, and capital gain. Nonetheless, investors are liable for reporting taxes locally.
Read our Australian crypto tax guide for more info on tax on Bitcoin mining.
Ben Knight

