The Ethereum Merge is one of the most highly anticipated events in the crypto market in the last few years which aims to make Ethereum ‘more scalable, more secure, and more sustainable’. Ethereum will transition from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus model, like Bitcoin, to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) model, which is expected to drastically reduce its environmental impact while improving network efficiency.
Despite the bear market, there is a tonne of buzz for the Merge, particularly after Ethereum developers confirmed it will take place around the week of September 15. In a nutshell, it is expected we’ll see a new and improved Ethereum that is:
- More environmentally friendly;
- More scalable;
- More decentralized; and
- Potentially a deflationary asset.
Background: Why the change?
Bitcoin and Ethereum, the two largest cryptocurrencies by market cap, have come under fire for how much energy they use. They both use a consensus mechanism known as Proof of Work where transactions are verified by miners who solve complex mathematical problems. Miners compete with each other to be the first to solve the problem with the winner receiving a reward paid out in cryptocurrency. While this consensus method is great for security, it is extremely energy inefficient as all energy spent by miners is essentially wasted.
The Merge will see Ethereum move to a Proof of Stake consensus mechanism, used by well-recognised blockchains such as Cardano, Solana, Polkadot, Tezos and Avalanche. It’s estimated that this will reduce Ethereum’s energy consumption by roughly 99.95%. Instead of competing to verify transactions, PoS blockchains selects participants to verify transactions based on the amount of crypto they’re staking.
This transition will also allow for scalability upgrades in the future I.e. quicker and cheaper transactions.
What is happening?
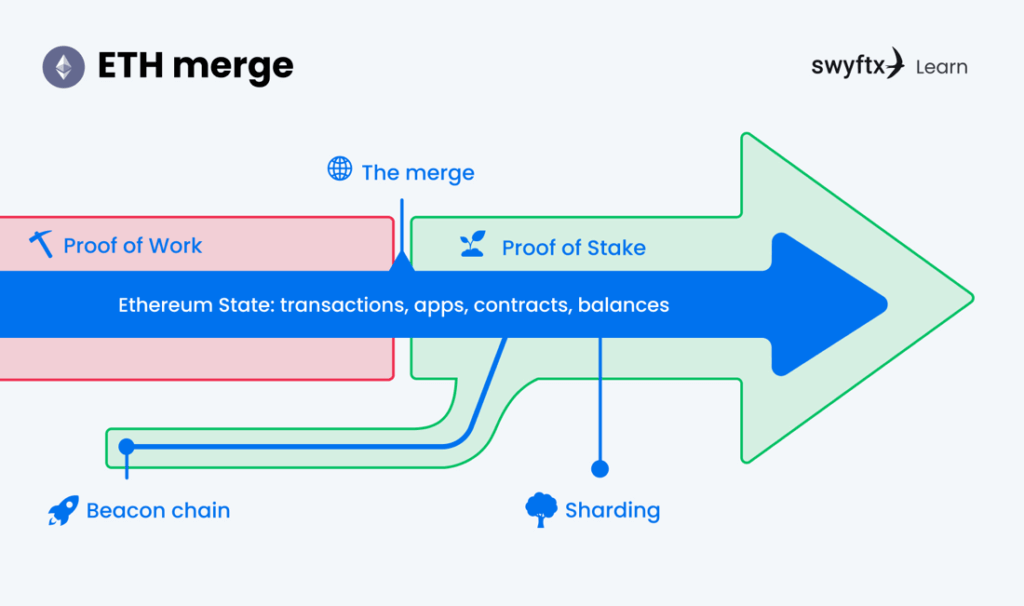
The Merge is the most significant upgrade to Ethereum ever. It refers to Ethereum’s transition from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake; which forms part of its roadmap to improve the scalability, security, and sustainability of the network.
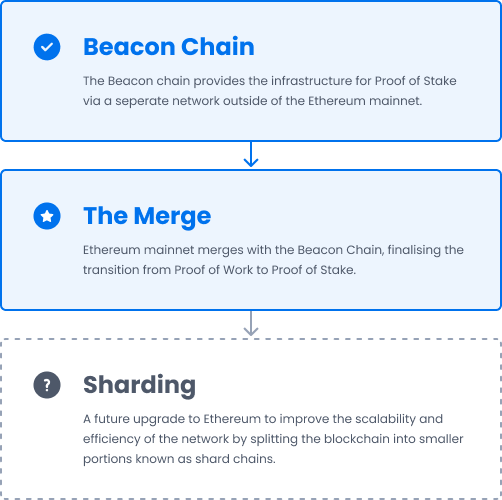
The Merge will occur when the existing Ethereum chain (the mainnet used today) joins with the Proof of Stake consensus layer which is known as the Beacon Chain. The Beacon chain provides the infrastructure for PoS and lays the foundation for sharding.
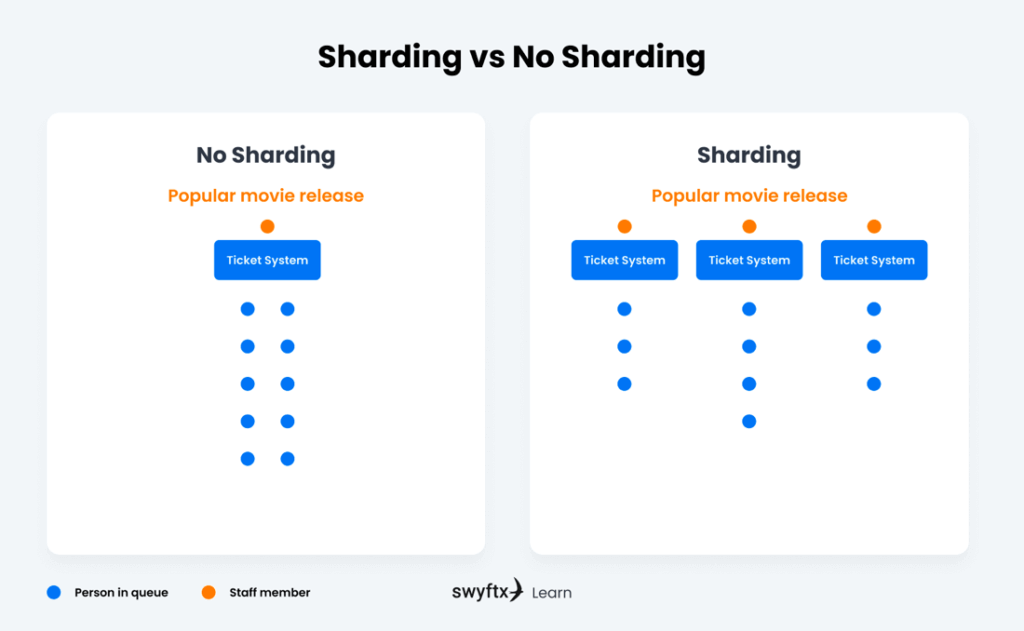
Sharding refers to splitting the Ethereum blockchain into multiple portions called ‘shards.’ This is a method that seeks to solve its issues with scalability, particularly with network congestion, which is the primary reason for high transaction fees and slow speeds.
A simple way of understanding sharding is thinking of it like a queue at a movie cinema. If only 1 person is working at the ticket desk, this would significantly slow down the speed of the queue. However, if several more registers are open, the queue will move far quicker.
When is it happening?
The Ethereum Merge is expected to occur around September 15th, although there is no set date as of yet. It has taken almost two years to reach this point, so any further minor delays would not be unexpected. The transition to a Proof of Stake consensus mechanism has already been achieved on various Ethereum testnets in preparation for the Merge.
It should be noted that the history from the original Ethereum mainnet will be preserved, as it is merged with the Beacon Chain. The entire transaction history of Ethereum will remain, so all funds will remain safe and secure.
In a best-case scenario, the Merge goes ahead as planned on time and without any critical issues.
Will Ethereum be deflationary?
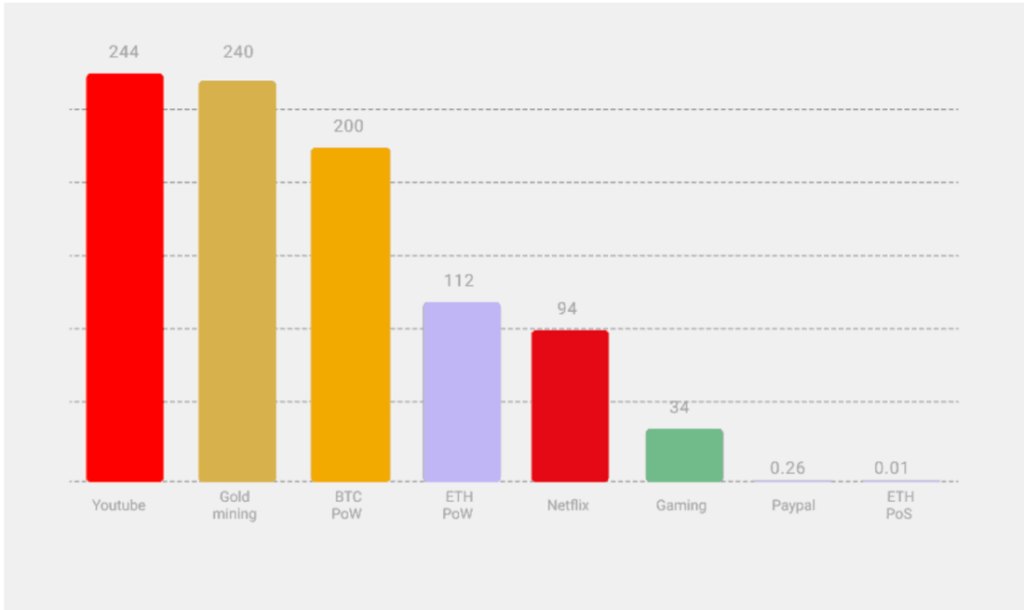
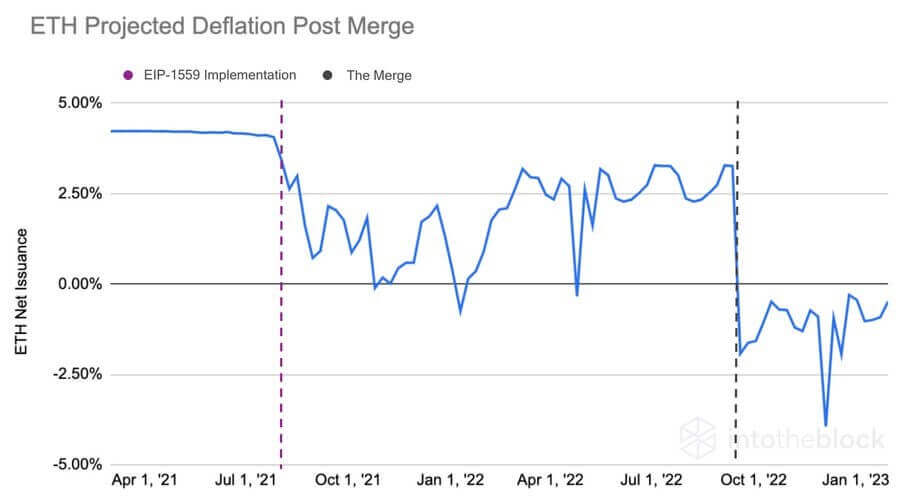
According to IntoTheBlock’s Lucas Outumuro, Ethereum will become a deflationary asset post Merge. This means the overall supply of ETH will shrink. From an economics perspective, when lower supply meets stable or rising demand, the value will tend to rise. However, even with the Merge, Ethereum will likely still be subject to the same volatility.
To break this down, in August 2021, Ethereum went through an upgrade called EIP-1559 which introduced a burning mechanism into ETH gas fees. This reduced the overall supply of ETH in the market and it is expected that the reduction in block rewards post Merge will continue to reduce the supply, resulting in Ethereum becoming a deflationary asset. The graphic below demonstrates this:
Misconceptions about the Merge
Since its announcement, there has been a lot of speculation about the Ethereum Merge, and many misconceptions have taken hold. Such misconceptions are mischievous at best, and damaging at worst, and here we wish to lay some of these to rest.
“The Merge will reduce gas fees”
First, the Merge is a change of the consensus mechanism—it is not an expansion of network capacity and will not result in lower gas fees (gas referring to the cost necessary to perform a transaction on the Ethereum network).
“Transactions will be faster post Merge”
Second, transactions will not be noticeably faster after the Merge. Though some slight changes will be made, transaction speed will remain, for the most part, as it is.
“The Merge will result in downtime of the blockchain”
Third, it has been proposed that the Merge will result in downtime of the chain. This is completely false, as a huge amount of work has been dedicated to ensuring that the Merge to Proof of Stake will be utterly seamless, so as not to affect users in the slightest.
For more information, Ethereum itself has compiled a list of various other misconceptions surrounding the upcoming Merge.
Ted

