Bitcoin is just over ten years old but it has already had a huge impact on the world. Many believe that Bitcoin is the future of money. Others claim that Bitcoin is just “magic internet money” with no inherent value. Bitcoin has been proclaimed dead by economist critics and the media ever since its release, but despite this Bitcoin continues to thrive. But what actually is Bitcoin? This guide will explore what Bitcoin is, how it began, and how it works.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer decentralized digital currency — the first of its kind in the world. This means that all Bitcoin transactions happen between equal, network participants without the need for a central authority like a central bank. This is made possible by using revolutionary blockchain technology, which was introduced by Bitcoin.
While Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency, it is certainly not the only one. Its widespread popularity and success has paved the way for thousands of other cryptocurrencies, or ‘altcoins’.
What can you use Bitcoin for?
Bitcoin has many of the same uses as fiat currencies. This means that you can use your Bitcoin as a medium of exchange to buy anything from coffee to cars, as long as the vendor accepts Bitcoin as payment. Another common use for Bitcoin is as a store of value. Many refer to Bitcoin as “digital gold”.
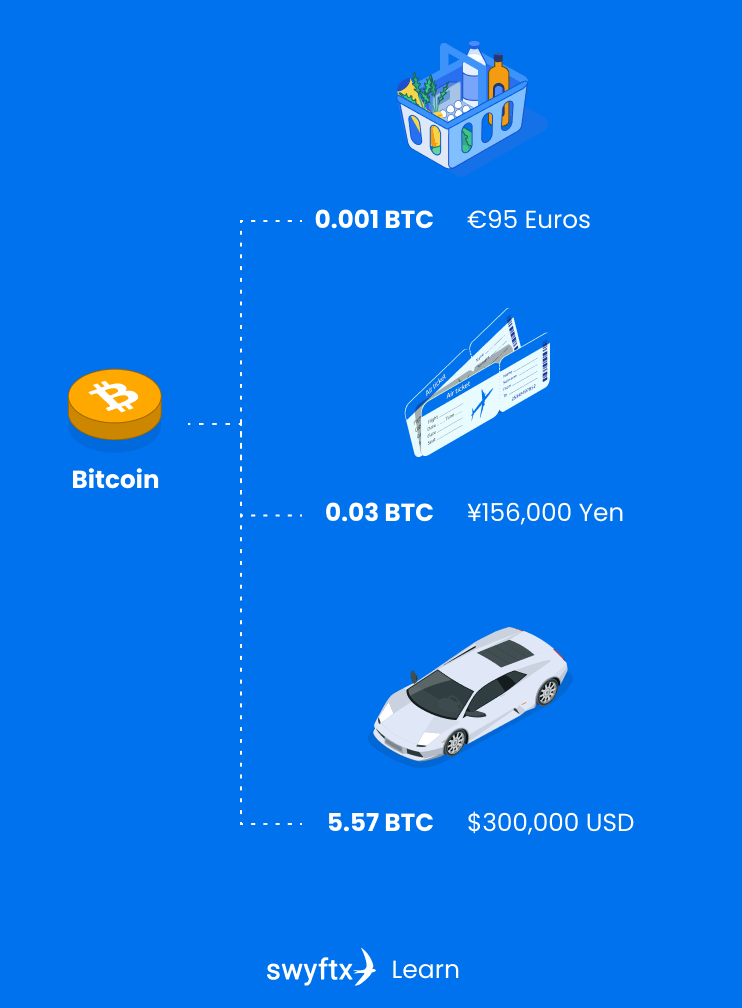
Figure 1 – Bitcoin as a medium of exchange
There are also several things that Bitcoin does better than fiat currencies. One example is remittances – the sending and receiving of money internationally. The cost of sending money internationally using Bitcoin is often much lower than other forms of remittance and can be done without the need to go through a bank.
One of the limitations of the Bitcoin network is that it can only process around 7 transactions per second (TPS). This pales in comparison to established payment networks like Visa and Paypal, and is a huge roadblock for Bitcoin becoming a legitimate everyday currency. Thankfully, this problem has been addressed by the Bitcoin lightning network, which takes a number of smaller or high-frequency transactions off the main blockchain and broadcasts them back in one efficient packet of data, vastly reducing congestion and improving TPS dramatically.
Key Takeaway
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency. It can be used like fiat currencies to pay for goods and services. It is also regarded as a store of value, like gold.
The benefits of Bitcoin
Bitcoin offers three key features that make it attractive:
- It is difficult to censor, as Bitcoins are the product of thousands of miners who operate around the world, who cannot easily be shut down.
- Bitcoin creates a new transaction every time funds move from one user to another, which means they can never be “double-spent” by fraudsters.
- Bitcoin transactions can be made at any time from anywhere in the world.
As a case example, people in some countries are restricted to how they can buy and sell products overseas because of bank limits. For example, say you’re living in Sydney and want to sell something to someone who lives in New York. Using traditional methods you would be charged exorbitant fees for currency conversion and there would usually be a time delay in getting your money as well.
Bitcoin solves this problem by being a global digital currency that can be purchased using AUD, U.S. dollars, Euros, Pounds, or other fiat currencies through Bitcoin exchanges and brokers. Furthermore, banking hours are irrelevant for Bitcoin, because the money is sent instantly.
The history of Bitcoin
Bitcoin was originally created by an anonymous developer, or group of developers, under the name Satoshi Nakamoto. Nakamoto believed that the world was heading in a direction of an all-digital economy and saw Bitcoin as a solution to some of its problems.
Nakamoto originally published a paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer To Peer Electronic Cash System” on October 31st, 2008. This paper would eventually become Bitcoin’s ‘whitepaper’. The abstract from the paper reads: “A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution.”
Did You Know?
The mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto is alleged to own at least 1 million Bitcoin. If this is true, Nakamoto is one of the richest people in the world.
How does Bitcoin work?
As Bitcoin is a digital currency, it does not have a physical form. It is decentralized, meaning it is not controlled by any government or bank, but rather by a network of users who verify and control transactions.
Proof of Work
Bitcoin uses a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which is used for validating transactions and mining new coins. Bitcoin’s system is comprised of a collection of computers, commonly referred to as “Bitcoin miners” or “nodes”, who are responsible for verifying transactions and creating new Bitcoins.
Bitcoin operates on a blockchain, which is a public ledger that records every Bitcoin transaction. As new blocks are mined, they are added to the blockchain and cannot be altered in any way.
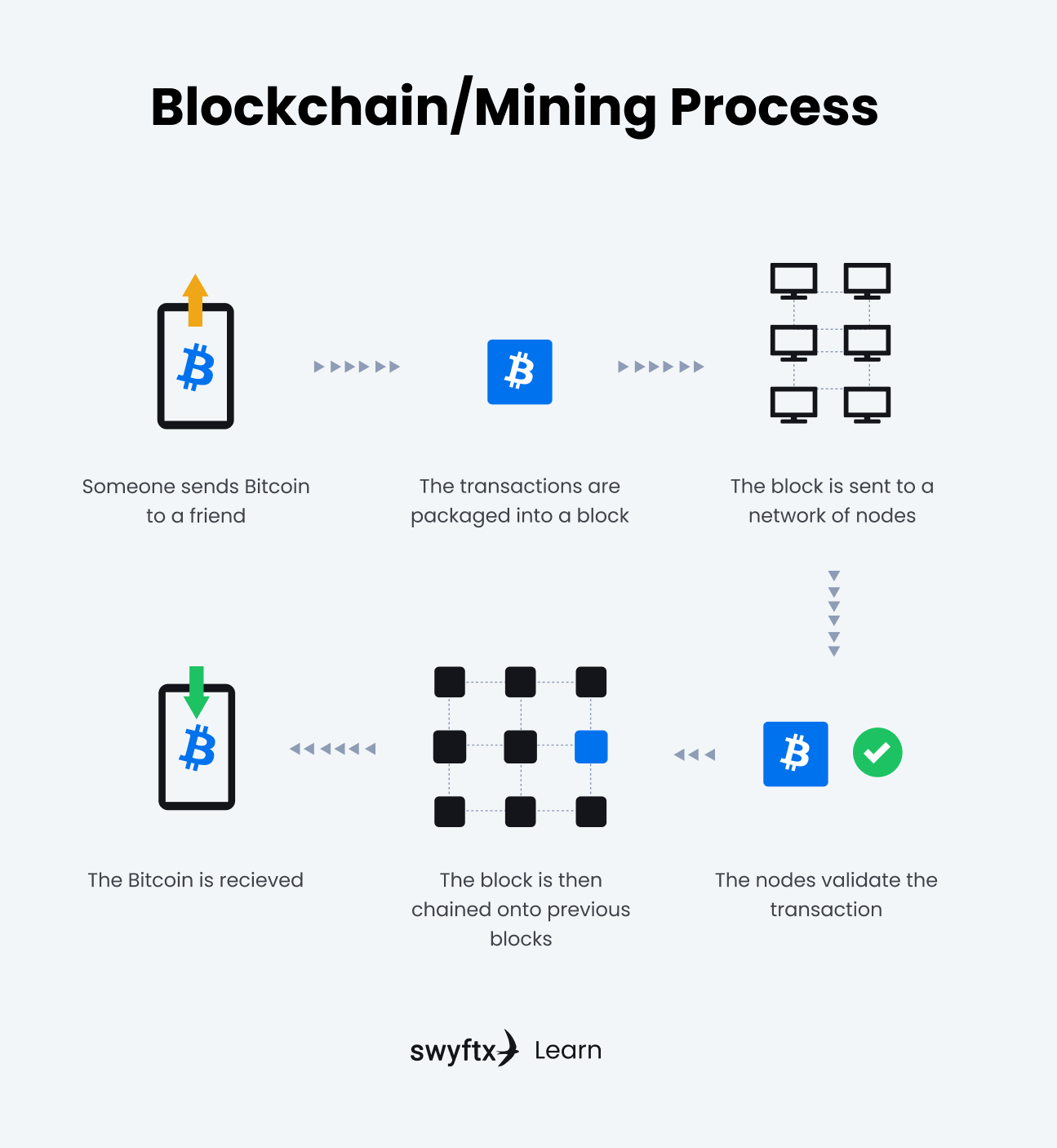
Figure 2 – The blockchain/mining process
P2P technology
Bitcoin uses peer-to-peer (P2P) technology to operate in a decentralized manner. P2P refers to the direct exchange of files, information, or assets without going through a central server or authority. Peer-to-peer also means that no one person can take control of the system, but rather it relies on cooperation from all users in order to function properly.
Digital wallets
All units of Bitcoin are stored in digital wallets. This is a software mechanism that is necessary for sending, receiving, and storing Bitcoin and other crypto assets. Every Bitcoin wallet has a public and private key. A public key is an address that identifies your account on the Bitcoin network, sort of like a bank account number. If someone is sending Bitcoin to your wallet, they will need this address. The private key can be thought of as similar to a bank PIN. It serves as a unique password that is required to access the funds within your wallet.
How is Bitcoin created?
Bitcoin is created using a process called Bitcoin mining, which involves using computing power to solve mathematical problems on the Bitcoin network. Every time a new block is mined, it creates Bitcoins, which miners receive as a reward for contributing their computing power to the Bitcoin network.
Key Takeaway
Bitcoin mining uses computational power from users around the world to solve complex mathematical problems in order to verify transactions and create new coins. Miners who successfully solve problems are rewarded with Bitcoin for their contributions.
When the Bitcoin network began in 2009, the block reward was a whopping 50 BTC, which was rewarded to the successful miner. As a core function of Bitcoin’s deflationary design, this reward is halved roughly every four years (every 210,000 blocks), which increases scarcity and demand and this has historically resulted in a price surge.
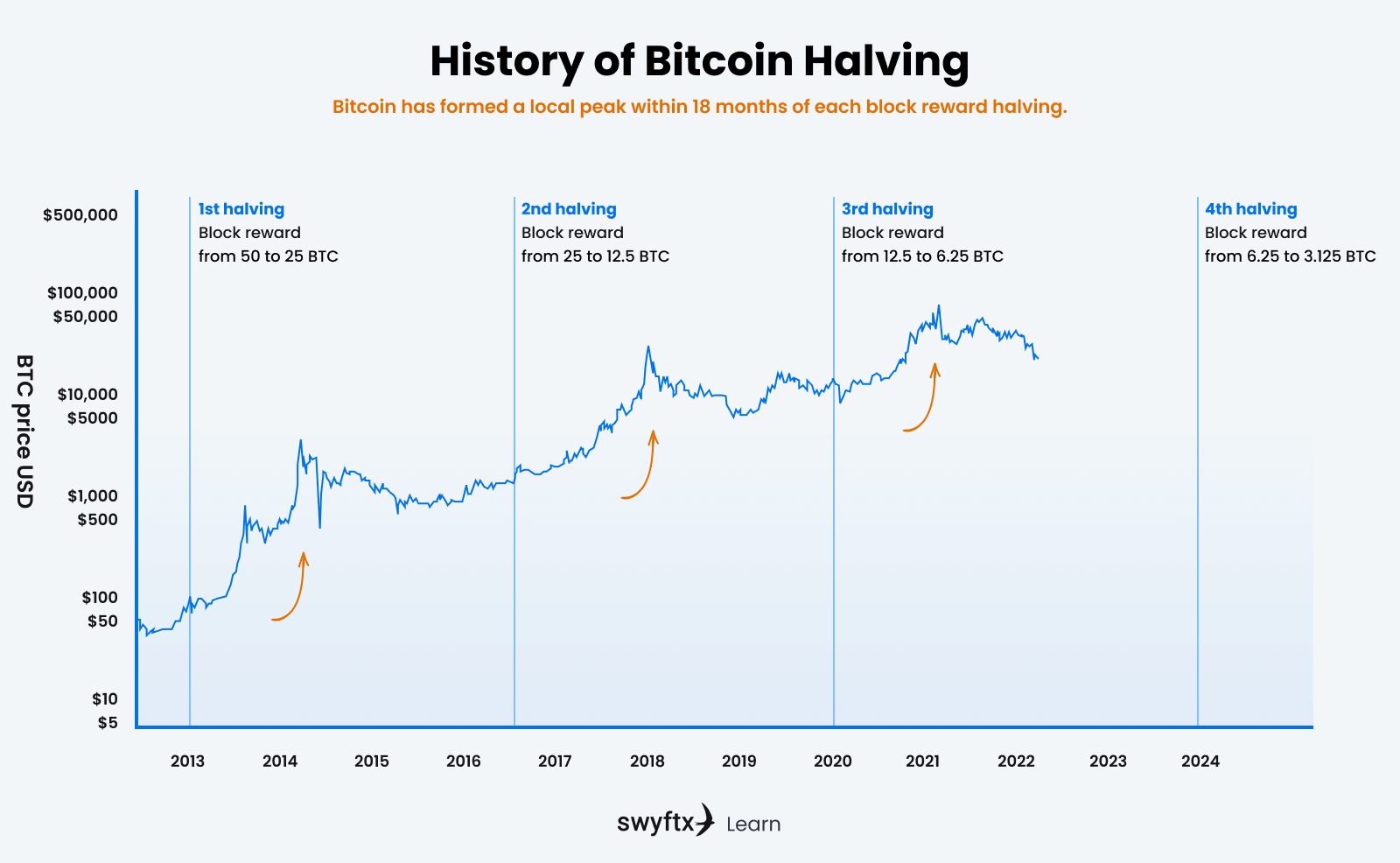
Figure 3 – Price action following Bitcoin halvings
How many Bitcoins are there?
Bitcoin has a maximum supply of 21 million. There are currently over 19 million Bitcoins in circulation and 54 million users on the Bitcoin network. These numbers are expected to continue to grow as more people and organisations become aware of the benefits of Bitcoin and join the network.
Is Bitcoin legal?
In most countries, Bitcoin is legal. It is, however, often considered a capital gain asset and is therefore subject to tax in most countries. China has heavily restricted the use of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. These crackdowns came in 2021 and meant that Bitcoin mining had to relocate to other areas of the globe, given that the majority of mining had previously taken place in China.
Where can I buy Bitcoin?
The most common way to buy and sell Bitcoin is through cryptocurrency exchanges or brokers. Swyftx is a crypto exchange that allows people from Australia and New Zealand to purchase Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies with low fees and market spreads. Swyftx users can deposit money into their account via a number of payment methods including bank transfer, POLi, PayID, or debit card.
Summary
Bitcoin is regarded by many to be the future of money. This is largely due to its introduction of blockchain technology, which allows people to send money to each other through a decentralized network of computers, without the need for a third party like a bank. This guide has explained what Bitcoin is, how it started, and how Bitcoin works. If you would like to learn more about blockchain technology, mining, or digital wallets, there is plenty more great content on Swyftx Learn!
Next lesson
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.
 Article read
Article read